Henderson–Hasselbalch Equation Using Log Acidity Constant
The Henderson–Hasselbalch equation describes the derivation of pH as a measure of acidity (using pKa, the negative log of the acid dissociation constant) in biological and chemical systems.
The pH equals the base 10 logarithm of the ratio between the base concentration and the acid concentration plus the log acidity constant.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 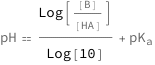 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= |  |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["pH", "Unitless"] == Log[QuantityVariable["[B]", "Molarity"]/QuantityVariable["[HA]", "Molarity"]]/Log[10] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["pK", "a"], "Unitless"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/ea0/ea06a700-e3fa-4cf1-859e-22ee9f318535/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

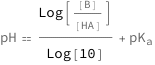
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Henderson\[Dash]Hasselbalch Equation Using Log Acidity Constant"], \
{QuantityVariable["[HA]","Molarity"] ->
Quantity[0.75`, ("Moles")/("Liters")]}]](images/ea0/ea06a700-e3fa-4cf1-859e-22ee9f318535-io-3-i.en.gif)
