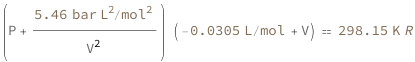Van der Waals Equation
The van der Waals equation is a thermodynamic equation of state that is based on the theory that fluids are composed of particles with nonzero volumes, and subject to a (not necessarily pairwise) interparticle attractive force.
The sum of the van der Waals constant a divided by the volume squared and the pressure times the difference of the volume and the van der Waals constant b equals the molar gas constant times the temperature.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 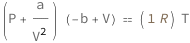 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 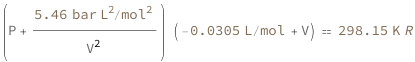 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard (QuantityVariable["P", "Pressure"] + QuantityVariable["a", "VanDerWaalsConstantA"]/QuantityVariable["V", "MolarVolume"]^2)*(-QuantityVariable["b", "VanDerWaalsConstantB"] + QuantityVariable["V", "MolarVolume"]) == Quantity[1, "MolarGasConstant"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/e5f/e5f126cf-8976-4125-996a-78450fbd09df/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Van der Waals Equation"], {QuantityVariable[
"a","VanDerWaalsConstantA"] ->
Quantity[5.46`, ("Bars" ("Liters")^2)/("Moles")^2],
QuantityVariable["b","VanDerWaalsConstantB"] ->
Quantity[0.0305`, ("Liters")/("Moles")],
QuantityVariable["T","Temperature"] ->
Quantity[298.15`, "Kelvins"]}]](images/e5f/e5f126cf-8976-4125-996a-78450fbd09df-io-3-i.en.gif)