Hohmann Exit Delta-V
The Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit used to transfer between two circular orbits of different radii in the same plane. The exit delta-v is the change in velocity needed to exit the elliptical orbit.
The Hohmann exit delta-v increases with the square root of the mass of the orbit center. As the radius of the inner and outer orbit increases, the delta-v decreases.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 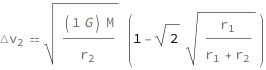 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 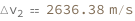 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Row[{"Δ", Subscript["v", "2"]}], "Speed"] == Sqrt[(Quantity[1, "GravitationalConstant"]*QuantityVariable["M", "Mass"])/QuantityVariable[Subscript["r", "2"], "Length"]]*(1 - Sqrt[2]*Sqrt[QuantityVariable[Subscript["r", "1"], "Length"]/(QuantityVariable[Subscript["r", "1"], "Length"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["r", "2"], "Length"])])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/d45/d4532ad4-3b04-4cc5-95ab-49ba60d99618/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

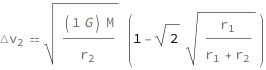
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject["Hohmann Exit Delta-V"], {QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("r"\), \("2"\)]\),"Length"] ->
Quantity[1.52`, "AstronomicalUnit"],
QuantityVariable["M","Mass"] ->
Quantity[1.988435`*^30, "Kilograms"], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("r"\), \("1"\)]\),"Length"] ->
Quantity[1, "AstronomicalUnit"]}]](images/d45/d4532ad4-3b04-4cc5-95ab-49ba60d99618-io-3-i.en.gif)