Newton's Law of Cooling
Newton's law of cooling states that the rate of heat loss of a body is directly proportional to the difference in the temperatures between the body and its surroundings, provided the temperature difference is small and the nature of the radiating surface remains the same.
The heat transfer rate equals the product of the area, heat transfer coefficient and the difference between the equilibrium temperature and the current temperature.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 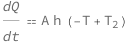 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 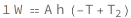 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Style["dQ", Italic]/Style["dt", Italic], "Power"] == QuantityVariable["A", "Area"]*QuantityVariable["h", "HeatTransferCoefficient"]*(-QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["T", "2"], "Temperature"])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/d3e/d3e6ec51-0c8c-4320-96a3-f5f7ff949fef/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
