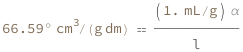Specific Rotation Using Pure Liquid
Specific rotation is a property of a chiral chemical compound. It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane-polarized light, per unit distance–concentration product, as the light passes through a sample of a compound in a solution.
Specific rotation equals the optical rotation angle divided by the density of the liquid and path length of the light.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 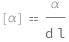 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 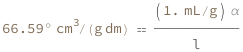 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["[α]", "SpecificRotation"] == QuantityVariable["α", "Angle"]/(QuantityVariable["d", "MassDensity"]*QuantityVariable["l", "PathLength"])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/cd7/cd7cad36-8605-4718-a1a6-ad5ea2908960/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Specific Rotation Using Pure Liquid"], {QuantityVariable[
"d","MassDensity"] -> Quantity[1.`, ("Grams")/("Milliliters")],
QuantityVariable["[\[Alpha]]","SpecificRotation"] ->
Quantity[66.59`, ("AngularDegrees" ("Centimeters")^3)/(
"Decimeters" "Grams")]}]](images/cd7/cd7cad36-8605-4718-a1a6-ad5ea2908960-io-3-i.en.gif)