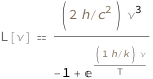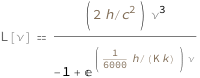Planck's Radiation Law Using Frequency
Planck's law describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a blackbody in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature.
The spectral radiance as a function of frequency is proportional to the frequency cubed divided by the sum of negative 1 and the exponential of the product of the frequency and the Planck constant divided by the temperature and the Boltzmann constant.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 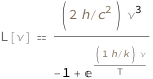 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 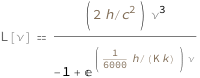 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["L"["ν"], "RadioBrightness"] == (Quantity[2, "PlanckConstant"/"SpeedOfLight"^2]*QuantityVariable["ν", "Frequency"]^3)/(-1 + E^((Quantity[1, "PlanckConstant"/"BoltzmannConstant"]*QuantityVariable["ν", "Frequency"])/QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]))](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/b2d/b2d6dae5-979c-4768-9672-b2232aa71a7e/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)