Perfectly Inelastic Collision
An inelastic collision is a collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved due to the action of internal friction. A perfectly inelastic collision occurs when the maximum amount of kinetic energy of a system is lost. In a perfectly inelastic collision, the colliding particles stick together.
The product of the mass and initial velocity of the first object plus the product of the mass and initial velocity of the second object equals the sum of the masses of the two objects times their final velocity.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 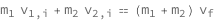 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 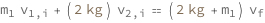 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["m", "1"], "Mass"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "1,i"], "Speed"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["m", "2"], "Mass"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "2,i"], "Speed"] == (QuantityVariable[Subscript["m", "1"], "Mass"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["m", "2"], "Mass"])*QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "f"], "Speed"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/a69/a69853d7-cfd3-42cf-9fdd-5048b4df552a/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
