Self-Inductance of Two Parallel Wires
The selfinductance of two parallel wires is a property that describes the electromotive force caused by the change in current in the wires.
The self\[Hyphen]inductance increases linearly with the length of the wires and logarithmically with the ratio of the distance between the wires and the radius of the wires.
Formula
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["L", "MagneticInductance"] == Log[QuantityVariable["d", "Distance"]/QuantityVariable["r", "Radius"]]*Quantity[Pi^(-1), "MagneticConstant"]*QuantityVariable["l", "Length"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/1cd/1cda7cff-e0b4-43ad-8fc1-bebb36e01b04/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
Forms
Examples
Get the resource:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 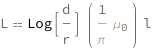 |
Use some values:
| In[3]:= | ![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Self-Inductance of Two Parallel Wires"], {QuantityVariable[
"r","Radius"] -> Quantity[0.5`, "Centimeters"],
QuantityVariable["l","Length"] -> Quantity[5, "Meters"],
QuantityVariable["d","Distance"] -> Quantity[25, "Centimeters"]}]](images/1cd/1cda7cff-e0b4-43ad-8fc1-bebb36e01b04-io-3-i.en.gif) |
| Out[3]= |