Rayleigh Flow
Rayleigh flow refers to frictionless, nonadiabatic flow through a constant area duct where the effect of heat addition or rejection is considered.
The ratio of pressure and choked pressure decreases quadratically as the Mach number increases, and is modified by the heat capacity ratio. The ratio of temperature and choked temperature increases quadratically with the heat capacity ratio, and is modified by the Mach number. The ratio of velocity and choked velocity, the ratio of density and choked density, and the ratio of stagnation and choked stagnation pressure depend on the Mach number and heat capacity ratio.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 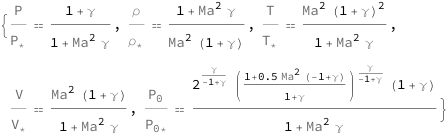 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 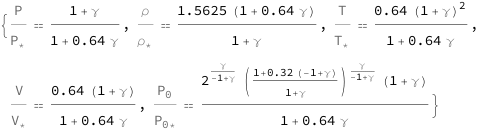 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard {QuantityVariable["P"/Subscript["P", "*"], "Unitless"] == (1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])/(1 + QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]), QuantityVariable["ρ"/SubStar["ρ"], "Unitless"] == (1 + QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])/(QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*(1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])), QuantityVariable["T"/SubStar["T"], "Unitless"] == (QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*(1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])^2)/(1 + QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]), QuantityVariable["V"/SubStar["V"], "Unitless"] == (QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*(1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))/(1 + QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]), QuantityVariable[Subscript["P", "0"]/Subscript["P", "0*"], "Unitless"] == (2^(QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]/(-1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))*((1 + 0.5*QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*(-1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))/(1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))^(QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]/(-1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))*(1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))/(1 + QuantityVariable["Ma", "MachNumber"]^2*QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/19a/19a48a82-3fd1-42f6-a0bb-a472e1d10dba/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)