Law of Cosines
The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles.
The square of the length of the third side equals the length of the first side squared plus the length of the second side squared minus twice the product of the length of the first side, the length of the second side and the cosine of the angle opposite the third side.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 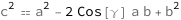 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 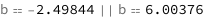 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["c", "Length"]^2 == QuantityVariable["a", "Length"]^2 - 2*Cos[QuantityVariable["γ", "Angle"]]*QuantityVariable["a", "Length"]*QuantityVariable["b", "Length"] + QuantityVariable["b", "Length"]^2](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/08a/08a0a3c1-d6b2-4b18-a799-724e5e4aa7a6/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
