Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas Using Particle Number
The internal energy of a system is the energy contained within the system, excluding the kinetic energy of motion of the system as a whole and the potential energy of the system as a whole due to external force fields. An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles whose only interactions are perfectly elastic collisions.
Internal energy of an ideal gas equals the product of the Boltzmann constant, particle number, temperature and the dimensionless specific heat capacity at constant volume (approximately 3/2 for a monatomic gas, 5/2 for diatomic gas and 7/2 for more complex molecules).
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 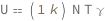 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 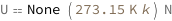 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["U", "Energy"] == Quantity[1, "BoltzmannConstant"]*QuantityVariable["N", "Unitless"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]*QuantityVariable["γ", "Unitless"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/9ca/9cad56af-8471-4d59-bcfc-60d19ad67240/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas Using Particle Number"], \
{QuantityVariable["T","Temperature"] -> Quantity[273.15`, "Kelvins"],
QuantityVariable["\[Gamma]","Unitless"] -> None}]](images/9ca/9cad56af-8471-4d59-bcfc-60d19ad67240-io-3-i.en.gif)