Bose–Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting Bosons Using Pressure
The Bose–Einstein condensation temperature is the temperature at which a free Bose gas transitions to a Bose–Einstein condensate. Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point macroscopic quantum phenomena become apparent.
The Bose-Einstein condensation temperature increases as the square of the cubic root of pressure increases, and increases inversely with the mass of each boson.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 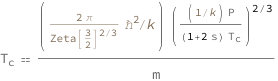 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 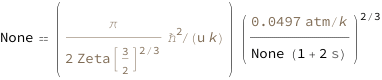 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["T", "c"], "Temperature"] == (Quantity[(2*Pi)/Zeta[3/2]^(2/3), "ReducedPlanckConstant"^2/"BoltzmannConstant"]*((Quantity[1, "BoltzmannConstant"^(-1)]*QuantityVariable["P", "Pressure"])/((1 + 2*QuantityVariable["s", "Unitless"])*QuantityVariable[Subscript["T", "c"], "Temperature"]))^(2/3))/QuantityVariable["m", "Mass"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/91b/91ba24a7-3022-41e4-ad51-5cece042487d/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Bose\[Dash]Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting \
Bosons Using Pressure"]]](images/91b/91ba24a7-3022-41e4-ad51-5cece042487d-io-2-i.en.gif)
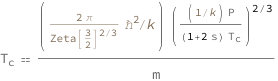
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Bose\[Dash]Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting \
Bosons Using Pressure"], {QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("T"\), \("c"\)]\),"Temperature"] -> None,
QuantityVariable["P","Pressure"] ->
Quantity[0.0497`, "Atmospheres"],
QuantityVariable["m","Mass"] -> Quantity[4, "AtomicMassUnit"]}]](images/91b/91ba24a7-3022-41e4-ad51-5cece042487d-io-3-i.en.gif)