Bell Coleman Cycle
The Bell Coleman cycle is a Brayton cycle driven in reverse, via network input, with air as the working fluid. Also called a gas refrigeration cycle, its purpose is to move heat, rather than produce work.
The thermal efficiency of a Bell Coleman cycle increases as the ratio of pressures approaches 1 as well as depends on the heat capacity ratio.
Formula
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["η", "th"], "ThermalEfficiency"] == (-1 + (QuantityVariable[Subscript["p", "h"], "Pressure"]/QuantityVariable[Subscript["p", "l"], "Pressure"])^((-1 + QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"])/QuantityVariable["γ", "HeatCapacityRatio"]))^(-1)](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/855/855a50a1-c2e5-4999-acb7-a47e71cdf7fd/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
| symbol | description | physical quantity |
|---|---|---|
| ηth | thermal efficiency | "ThermalEfficiency" |
| ph | high pressure | "Pressure" |
| pl | low pressure | "Pressure" |
| γ | heat capacity ratio | "HeatCapacityRatio" |
Forms
Examples
Get the resource:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 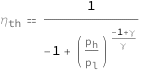 |
Use some values:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 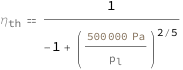 |