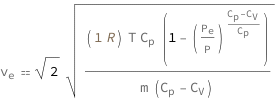De Laval Nozzle
A de Laval nozzle is a tube that is pinched in the middle, making a carefully balanced, asymmetric hourglass shape. It is used to accelerate a hot, pressurized gas passing through it to a higher supersonic speed in the axial (thrust) direction, by converting the heat energy of the flow into kinetic energy.
Exhaust gas velocity from a de Laval nozzle increases with the square root of the temperature, and inversely with the square root of the molar mass. The heat capacity also plays a major part, increasing as the isobaric and isochoric heat capacities converge. Increasing inlet pressure or decreasing exhaust pressure also increase the velocity.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 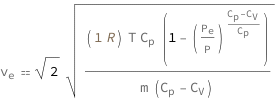 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= |  |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "e"], "Speed"] == Sqrt[2]*Sqrt[(Quantity[1, "MolarGasConstant"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "p"], "HeatCapacity"]*(1 - (QuantityVariable[Subscript["P", "e"], "Pressure"]/QuantityVariable["P", "Pressure"])^((QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "p"], "HeatCapacity"] - QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "V"], "HeatCapacity"])/QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "p"], "HeatCapacity"])))/(QuantityVariable["m", "MolarMass"]*(QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "p"], "HeatCapacity"] - QuantityVariable[Subscript["C", "V"], "HeatCapacity"]))]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/7f9/7f99dbca-a21b-4bca-b1a8-8b9ad96a04b3/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)