Joule's Law Using Electric Potential
Joule's first law states that the power of heating generated by an electrical conductor is proportional to the product of its resistance and the square of the current.
Heat equals power times time. Power equals the electric potential difference squared divided by the electric resistance.
Formula
![Copy to Clipboard {QuantityVariable["Q", "Heat"] == QuantityVariable["P", "Power"]*QuantityVariable["t", "Time"], QuantityVariable["P", "Power"] == QuantityVariable["U", "ElectricPotential"]^2/QuantityVariable["R", "ElectricResistance"]}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/7f8/7f898db4-6b65-42a2-992d-9ef00b3d626b/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
| symbol | description | physical quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Q | heat | "Heat" |
| P | power | "Power" |
| t | time | "Time" |
| R | electric resistance | "ElectricResistance" |
| U | electric potential difference | "ElectricPotential" |
Forms
Examples
Get the resource:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Use some values:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 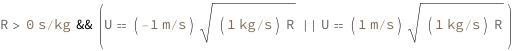 |