Nernst Equation Using Equilibrium Constant
The Nernst equation is an equation that relates the reduction potential of an electrochemical reaction (half-cell or full-cell reaction) to the standard electrode potential, temperature and activities (often approximated by concentrations) of the chemical species undergoing reduction and oxidation.
The standard cell potential equals the logarithm of the equilibrium constant times the product of the molar gas constant and temperature divided by the product of the number of electrons transferred and the Faraday constant.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 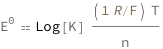 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 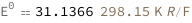 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Superscript["E", "0"], "ElectricPotential"] == Row[{Log[QuantityVariable["K", "Unitless"]]}]*Row[{(Quantity[1, "MolarGasConstant"/"FaradayConstant"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"])/QuantityVariable["n", "Unitless"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/78c/78c11df7-72dd-4f60-8584-823bd8cb01cf/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Nernst Equation Using Equilibrium Constant"], {QuantityVariable[
"T","Temperature"] -> Quantity[298.15`, "Kelvins"],
QuantityVariable["K","Unitless"] -> 3.33`3.*^13,
QuantityVariable["n","Unitless"] -> 1}]](images/78c/78c11df7-72dd-4f60-8584-823bd8cb01cf-io-3-i.en.gif)