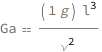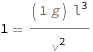Galileo Number Using Characteristic Length
The Galileo number is proportional to gravity forces divided by viscous forces. The Galileo number is used in viscous flow and thermal expansion calculations—for example, to describe fluid film flow over walls. These flows apply to condensors or chemical columns.
The Galileo number equals the characteristic length cubed times the acceleration of gravity divided by the kinematic viscosity squared.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 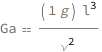 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 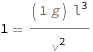 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["Ga", "GalileoNumber"] == (Quantity[1, "StandardAccelerationOfGravity"]*QuantityVariable["l", "Length"]^3)/QuantityVariable["ν", "KinematicViscosity"]^2](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/721/7219bef7-5827-4298-8873-0d30677cd618/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)