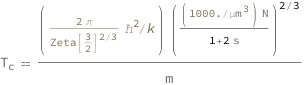Bose–Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting Bosons Using Volume
The Bose–Einstein condensation temperature is the temperature at which a free Bose gas transitions to a Bose–Einstein condensate. Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point macroscopic quantum phenomena become apparent.
The Bose-Einstein condensation temperature increases as the square of the cubic root of the ratio between particle number and volume increases, and increases inversely with the mass of each boson.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 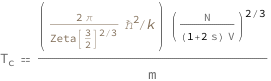 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 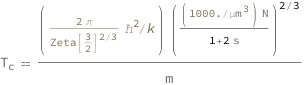 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["T", "c"], "Temperature"] == (Quantity[(2*Pi)/Zeta[3/2]^(2/3), "ReducedPlanckConstant"^2/"BoltzmannConstant"]*(QuantityVariable["N", "Unitless"]/((1 + 2*QuantityVariable["s", "Unitless"])*QuantityVariable["V", "Volume"]))^(2/3))/QuantityVariable["m", "Mass"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/5ce/5ceaf094-352f-4500-9fe1-591991c69b0b/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Bose\[Dash]Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting \
Bosons Using Volume"]]](images/5ce/5ceaf094-352f-4500-9fe1-591991c69b0b-io-2-i.en.gif)
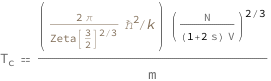
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Bose\[Dash]Einstein Condensation Temperature for Noninteracting \
Bosons Using Volume"], {QuantityVariable["V","Volume"] ->
Quantity[0.001`, ("Micrometers")^3]}]](images/5ce/5ceaf094-352f-4500-9fe1-591991c69b0b-io-3-i.en.gif)