Fourier Number Using Thermal Conductivity
The Fourier number is a dimensionless number that characterizes transient heat conduction. Conceptually, it is the ratio of diffusive or conductive transport rate to the quantity storage rate, where the quantity may be either heat (thermal energy) or matter (particles).
The Fourier number is the characteristic time interval times the thermal conductivity divided by the product of the specific heat capacity, the characteristic length squared and the mass density.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 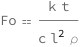 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= |  |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable["Fo", "FourierNumber"] == (QuantityVariable["k", "ThermalConductivity"]*QuantityVariable["t", "Time"])/(QuantityVariable["c", "SpecificHeatCapacity"]*QuantityVariable["l", "Length"]^2*QuantityVariable["ρ", "MassDensity"])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/349/3494320b-5f96-4edd-a6e8-43976e0a9c2b/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Fourier Number Using Thermal Conductivity"], {QuantityVariable[
"t","Time"] -> Quantity[1, "Seconds"],
QuantityVariable["l","Length"] -> Quantity[1, "Meters"],
QuantityVariable["c","SpecificHeatCapacity"] ->
Quantity[0.1`, ("Joules")/("KelvinsDifference" "Kilograms")],
QuantityVariable["\[Rho]","MassDensity"] ->
Quantity[1000, ("Kilograms")/("Meters")^3],
QuantityVariable["Fo","FourierNumber"] -> 1}]](images/349/3494320b-5f96-4edd-a6e8-43976e0a9c2b-io-3-i.en.gif)