Expanded Boiling-Point Elevation Equation
Boiling-point elevation describes the phenomenon in which the boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent. This formula assumes dilute ideal nonvolatile solutions.
Boiling-point elevation equals the product of the molar gas constant, solution molality, solvent molar mass and the square of the solvent boiling point divided by the solvent molar enthalpy of vaporization.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 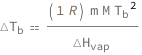 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= |  |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["ΔT", "b"], "TemperatureDifference"] == (Quantity[1, "MolarGasConstant"]*QuantityVariable["m", "Molality"]*QuantityVariable["M", "MolarMass"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["T", "b"], "Temperature"]^2)/QuantityVariable[Subscript["ΔH", "vap"], "MolarEnergy"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/2de/2de16de7-0c58-4e86-9ebd-f70f6f804ac6/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Expanded Boiling-Point Elevation Equation"], {QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("\[CapitalDelta]\[InvisibleSpace]T"\), \
\("b"\)]\),"TemperatureDifference"] ->
Quantity[1.`, "KelvinsDifference"],
QuantityVariable["M","MolarMass"] ->
Quantity[0.0180153`, ("Kilograms")/("Moles")]}]](images/2de/2de16de7-0c58-4e86-9ebd-f70f6f804ac6-io-3-i.en.gif)
