Multiple-Slit Diffraction Using Wavelength
Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit. It is defined as the bending of light around the corners of an obstacle or aperture into the region of the geometrical shadow of the obstacle. Multiple-slit diffraction occurs when a wave encounters several slits.
The normalized transmitted intensity decreases with the number of slits, the slit separation distance and the width of the slits. Increasing wavelength also increases the normalized transmitted intensity. The normalized transmitted intensity varies sinusoidally with the diffraction angle.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 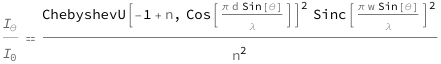 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 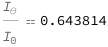 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript[Style["I", Italic], "θ"]/Subscript[Style["I", Italic], "0"], "Unitless"] == (ChebyshevU[-1 + QuantityVariable["n", "Unitless"], Cos[(Pi*QuantityVariable["d", "Distance"]*Sin[QuantityVariable["θ", "Angle"]])/QuantityVariable["λ", "Wavelength"]]]^2*Sinc[(Pi*QuantityVariable["w", "Distance"]*Sin[QuantityVariable["θ", "Angle"]])/QuantityVariable["λ", "Wavelength"]]^2)/QuantityVariable["n", "Unitless"]^2](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/056/056eecac-612b-41ac-be5d-1631bcbd52a4/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

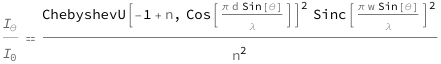
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Multiple-Slit Diffraction Using Wavelength"], {QuantityVariable[
"n","Unitless"] -> 2,
QuantityVariable["w","Distance"] -> Quantity[0.1`, "Millimeters"],
QuantityVariable["\[Theta]","Angle"] ->
Quantity[0.1`, "AngularDegrees"],
QuantityVariable["d","Distance"] -> Quantity[0.3`, "Millimeters"],
QuantityVariable["\[Lambda]","Wavelength"] ->
Quantity[500, "Nanometers"]}]](images/056/056eecac-612b-41ac-be5d-1631bcbd52a4-io-3-i.en.gif)