Wolfram Language Paclet Repository
Community-contributed installable additions to the Wolfram Language
QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
| | ||||
|
| | ||||
|
| | ||||
|
| | ||||
QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
QuantumState |
|
QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|

QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
QuantumState |

QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
QuantumState |
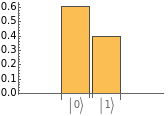
QuantumMeasurementOperator |
|
QuantumState |
