GloVe 50-Dimensional Word Vectors
Trained on
Tweets
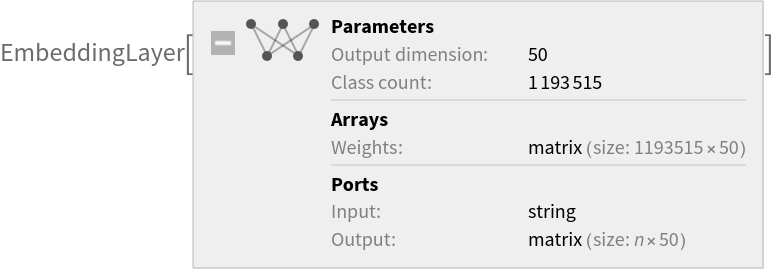
Released in 2014 by the computer science department at Stanford University, this 50-dimensional representation is trained using an original method called Global Vectors (GloVe). It encodes 1,193,515 tokens as unique vectors, with all tokens outside the vocabulary encoded as the zero-vector. Token case is ignored.
Number of layers: 1 |
Parameter count: 59,675,750 |
Trained size: 252 MB |
Examples
Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained net:
Basic usage
Use the net to obtain a list of word vectors:
Obtain the dimensions of the vectors:
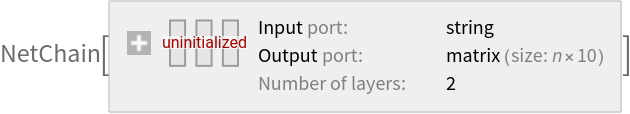
Use the embedding layer inside a NetChain:
Feature visualization
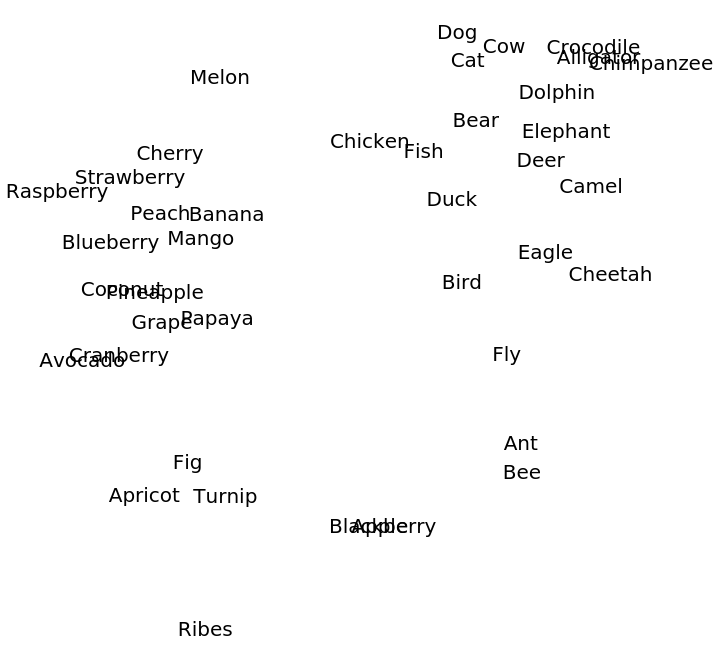
Create two lists of related words:
Visualize relationships between the words using the net as a feature extractor:
Word analogies
Get the pre-trained net:
Get a list of words:
Obtain the vectors:
Create an association whose keys are words and whose values are vectors:
Find the eight nearest words to "king":
Man is to king as woman is to:
France is to Paris as Germany is to:
Net information
Inspect the number of parameters of all arrays in the net:
Obtain the total number of parameters:
Obtain the layer type counts:
Export to MXNet
Export the net into a format that can be opened in MXNet:
Export also creates a net.params file containing parameters:
Get the size of the parameter file:
The size is similar to the byte count of the resource object:
Represent the MXNet net as a graph:
Requirements
Wolfram Language
11.2
(September 2017)
or above
Resource History
Reference