Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained network:
Basic usage
Predict the next character of a given sequence:
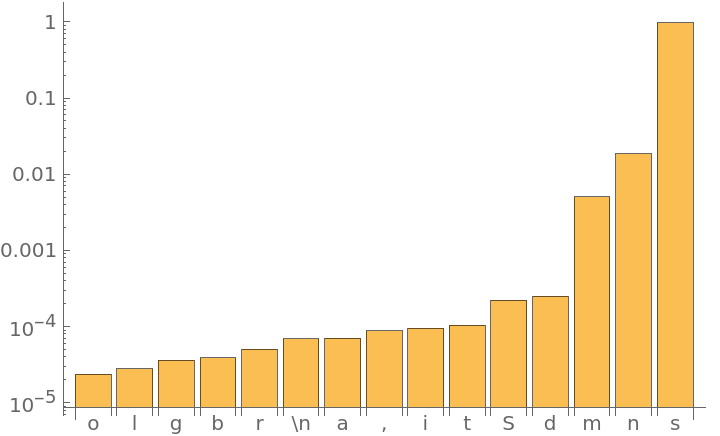
Get the top 15 probabilities:
Plot the top 15 probabilities:
Generation
Generate text efficiently with NetStateObject. A built-in option for temperature sampling is available in Wolfram Language 12.0, while it has to be implemented explicitly in earlier versions.
Generate for 100 steps using “def parse” as an initial string:
The third optional argument is a “temperature” parameter that scales the input to the final softmax. A high temperature flattens the distribution from which characters are sampled, increasing the probability of extracting less likely characters:
Decreasing the temperature sharpens the peaks of the sampling distribution, further decreasing the probability of extracting less likely characters:
Very high temperature settings are equivalent to random sampling:
Very low temperature settings are equivalent to always picking the character with maximum probability. It is typical for sampling to “get stuck in a loop”:
Inspection of predictions
Define a function that takes a string and guesses the next character as it reads, showing the predictions in a grid. The input string is shown on top, while the top 5 predictions are aligned below each character, starting from more likely guesses. For each prediction, the intensity of the color is proportional to the probability:
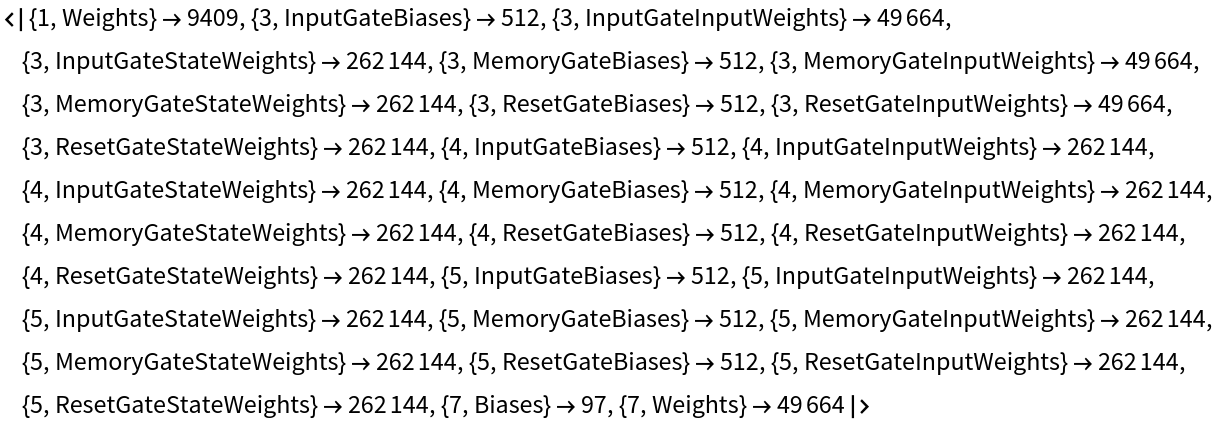
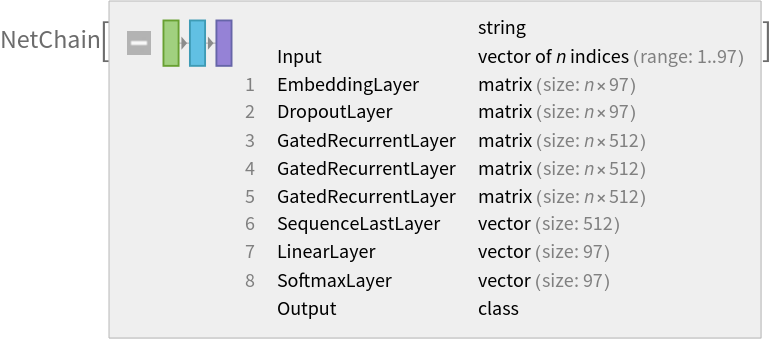
Net information
Inspect the sizes of all arrays in the net:
Obtain the total number of parameters:
Obtain the layer type counts:
Display the summary graphic:
Export to MXNet
Export the net into a format that can be opened in MXNet:
Export also creates a net.params file containing parameters:
Get the size of the parameter file:
The size is similar to the byte count of the resource object:

![generateSample[start_, len_, temp_ : 1] := Block[{net, score, sampler, obj},
net = NetModel["Wolfram Python Character-Level Language Model V1"];
If[$VersionNumber < 12.0,
score = NetTake[net, 7];
sampler = NetTake[net, -1];
obj = NetStateObject[score];
StringJoin@
NestList[sampler[obj[#]/temp, "RandomSample"] &, start, len],
obj = NetStateObject[net];
StringJoin@
NestList[obj[#, {"RandomSample", "Temperature" -> temp}] &, start,
len]
]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/99d/99d6d1ce-c523-41d7-a886-2a0b4db71e3a/62c9d2128e643592.png)





![inspectPredictions[string_] := Block[
{obj, chars, pred, predItems, charItems},
obj = NetStateObject[
NetModel["Wolfram Python Character-Level Language Model V1"]];
chars = Characters[string];
pred = Map[obj[#, {"TopProbabilities", 5}] &, chars] /. {"\n" -> "\\n", "\t" -> "\\t"};
predItems = Map[Item[First[#], Background -> Opacity[Last[#], Darker[Green]]] &, pred, {2}];
predItems = Prepend[Most[predItems], Table[Item["", Background -> Gray], 5]];
charItems = Item[#, Background -> LightBlue] & /@ (chars /. {"\n" -> "\\n", "\t" -> "\\t"});
Grid[
Prepend[Transpose[predItems], charItems],
Spacings -> {0.6, 0.2}, Dividers -> All, FrameStyle -> Gray
]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/99d/99d6d1ce-c523-41d7-a886-2a0b4db71e3a/2d0efe4979daebdb.png)