Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained net:
NetModel parameters
This model consists of a family of individual nets, each identified by a specific parameter combination. Inspect the available parameters:
Pick a non-default net by specifying the parameters:
Pick a non-default uninitialized net:
Basic usage
Classify an image:
The prediction is an Entity object, which can be queried:
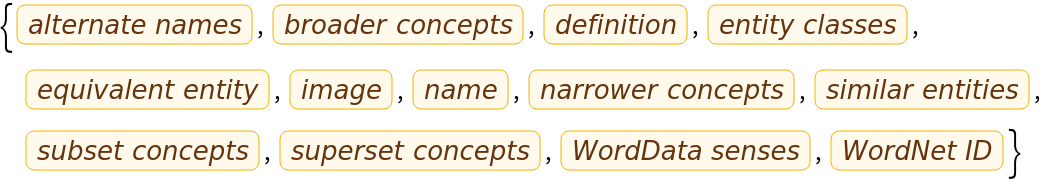
Get a list of available properties of the predicted Entity:
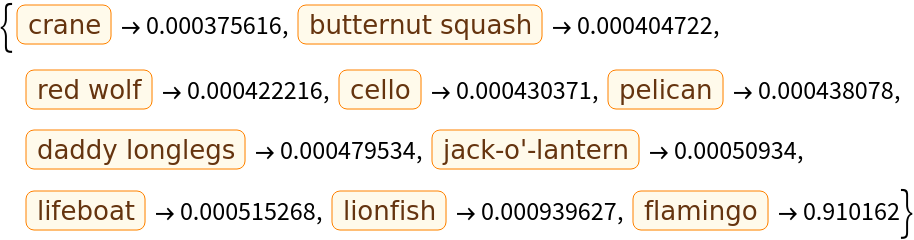
Obtain the probabilities of the 10 most likely entities predicted by the net:
An object outside the list of the ImageNet classes will be misidentified:
Obtain the list of names of all available classes:
Feature extraction
Remove the last two layers of the trained net so that the net produces a vector representation of an image:
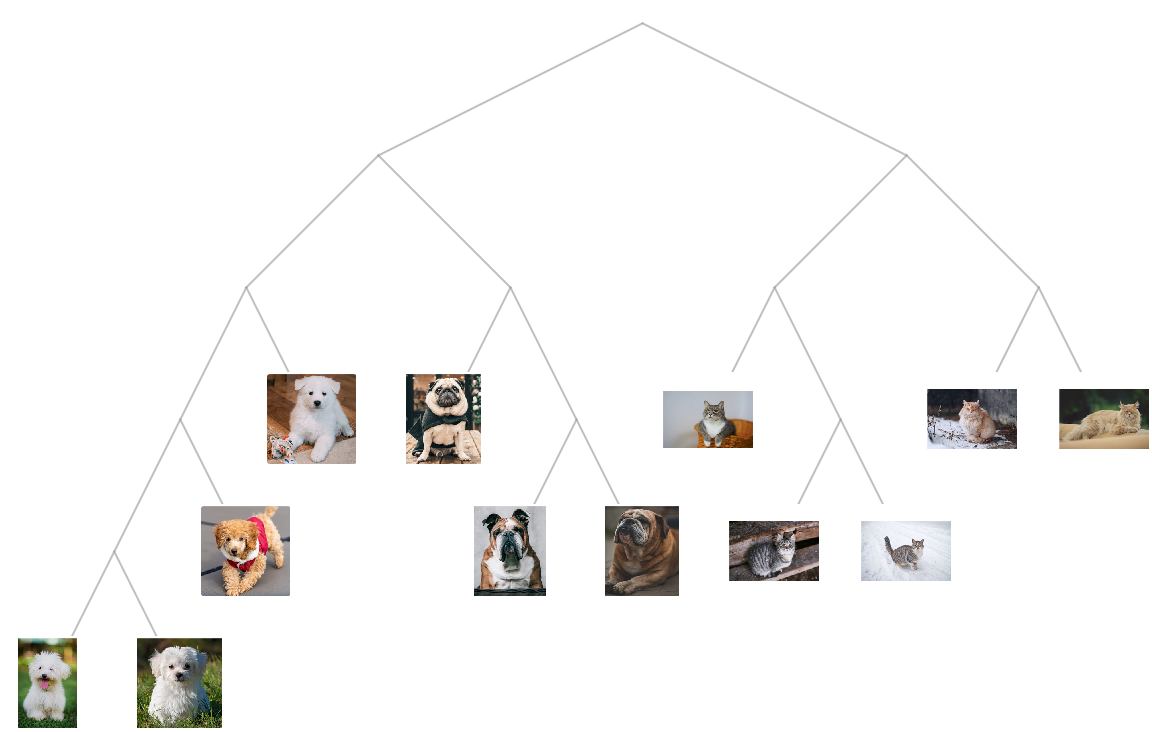
Get a set of images:
Use the net as a feature extractor to build a clustering tree of the images:
Transfer learning
Use the pre-trained model to build a classifier for telling apart indoor and outdoor photos. Create a test set and a training set:
Remove the linear layer from the pre-trained net:
Create a new net composed of the pre-trained net followed by a linear layer and a softmax layer:
Train on the dataset, freezing all the weights except for those in the "linearNew" layer (use TargetDevice -> "GPU" for training on a GPU):
Perfect accuracy is obtained on the test set:
Net information
Inspect the number of parameters of all arrays in the net:
Obtain the total number of parameters:
Obtain the layer type counts:
Export to ONNX
Export the net to the ONNX format:
Get the size of the ONNX file:
Check some metadata of the ONNX model:
Import the model back into the Wolfram Language. However, the NetEncoder and NetDecoder will be absent because they are not supported by ONNX:


![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/176c8658-0030-43cc-bd84-5825fa715e55"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/11d985c67dfcc42c.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/85377d40-587b-40e0-8487-15ce4a72161f"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/611db489dbf6d9aa.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/0f2aa57c-8166-412b-bb2d-6e15ce66d212"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/6878259fd1ed7a14.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/0e6e12b1-30d7-4797-bbd8-4f18ee34e049"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/24ae3f8876323fa6.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/a496e5c3-e3b0-4f4c-a3fa-bb1b369b4e32"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/620ef3134a99352e.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/937b0ed4-100e-4e1b-9e3a-e3be7b75a0a2"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/952/952534f9-192e-44a6-b574-9b860b0bd173/130dcb8219b53fe6.png)
