CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation
Trained on
ImageNet Competition Data
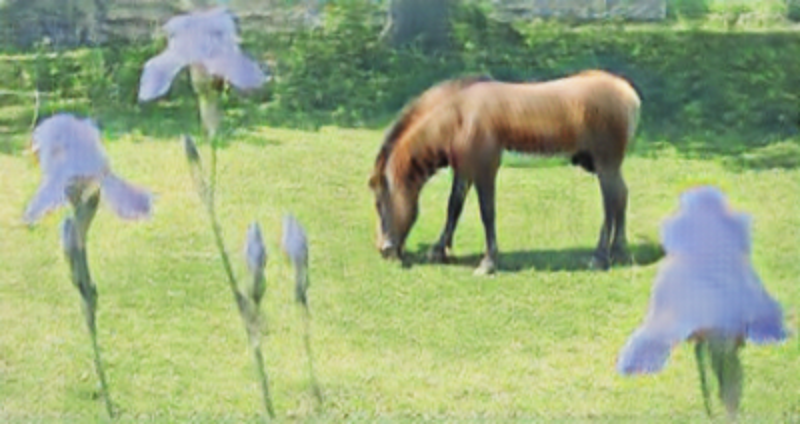
Released in 2017, this model exploits a novel technique for image translation, in which two models translating from A to B and vice versa are trained jointly with adversarial training. In addition to the adversarial loss, cycle consistency is also enforced in the loss function: when the output of the first translator is fed into the second, the final result is encouraged to match the input of the first translator. This allows successful training for image translation tasks in which only unpaired training data can be collected. This model was trained to translate zebras into horses.
Number of layers: 94 |
Parameter count: 2,855,811 |
Trained size: 12 MB |
Examples
Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained net:
Basic usage
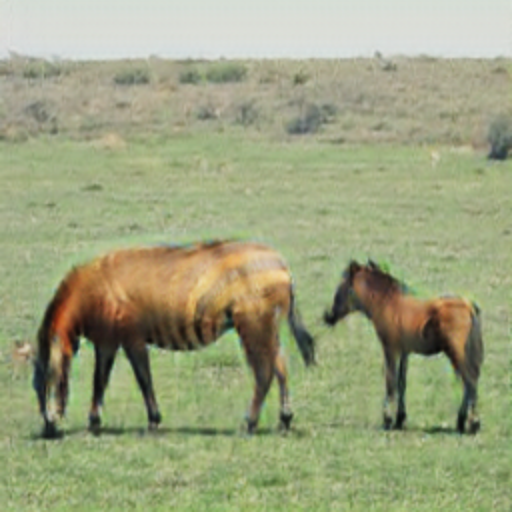
Run the net on a photo:
Adapt to any size
Automatic image resizing can be avoided by replacing the net encoders. First get the net:
Get a photo:
Create a new encoder with the desired dimensions:
Attach the new net encoder and run the network:
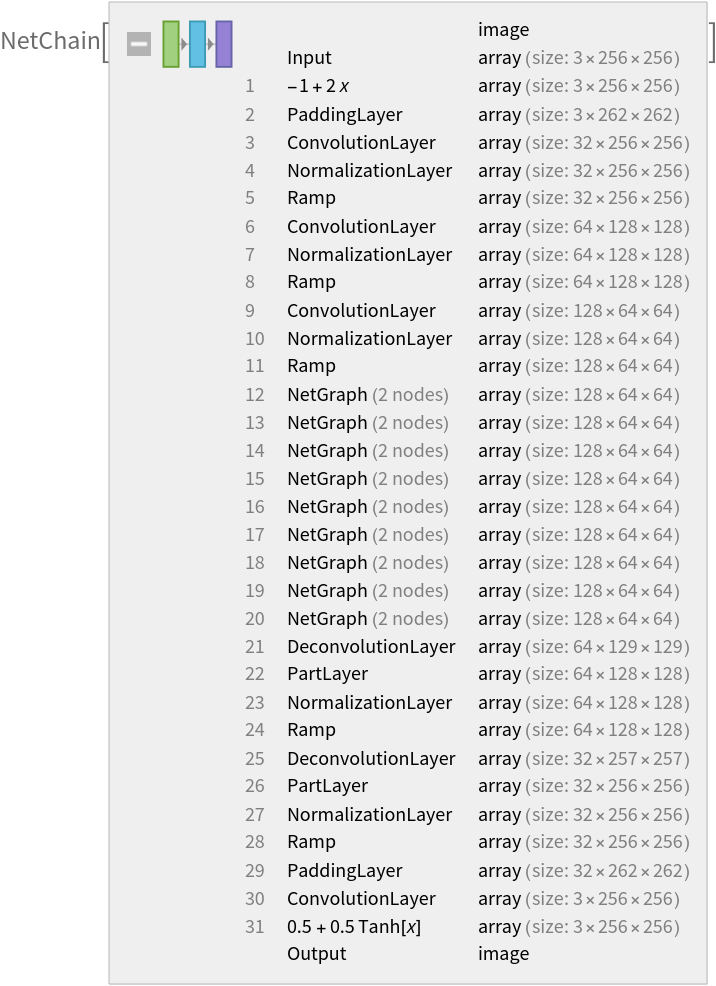
Net information
Inspect the sizes of all arrays in the net:
Obtain the total number of parameters:
Obtain the layer type counts:
Display the summary graphic:
Export to MXNet
Export the net into a format that can be opened in MXNet:
Export also creates a net.params file containing parameters:
Get the size of the parameter file:
The size is similar to the byte count of the resource object:
Represent the MXNet net as a graph:
Requirements
Wolfram Language
11.3
(March 2018)
or above
Resource History
Reference
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/e9c35577-a51a-4fd3-87d6-5471cdff177f"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/0bb1aa1dd936c127.png)

![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/3e8eb03e-cc55-402a-9b74-ec9ae3294d05"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/102f0a495b613fbb.png)

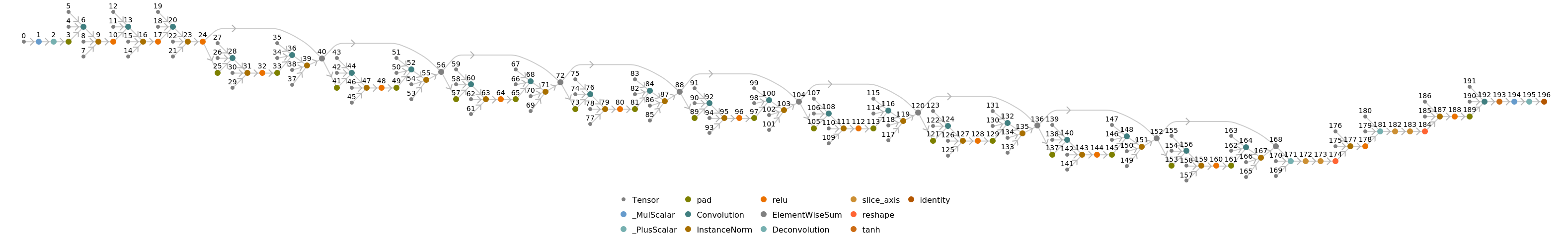
![NetInformation[
NetModel["CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation Trained on ImageNet \
Competition Data"], "ArraysSizes"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/707447d3b5a451d5.png)

![NetInformation[
NetModel["CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation Trained on ImageNet \
Competition Data"], "ArraysTotalElementCount"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/4bd8854683d3e59f.png)
![NetInformation[
NetModel["CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation Trained on ImageNet \
Competition Data"], "LayerTypeCounts"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/7533b8dba7e688e2.png)
![NetInformation[
NetModel["CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation Trained on ImageNet \
Competition Data"], "SummaryGraphic"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/00bfaa33a3b3731b.png)
![jsonPath = Export[FileNameJoin[{$TemporaryDirectory, "net.json"}], NetModel["CycleGAN Zebra-to-Horse Translation Trained on ImageNet \
Competition Data"], "MXNet"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4b1/4b148040-10cd-43e2-8152-1a31c675cec3/11b579e810c09973.png)