Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained net:
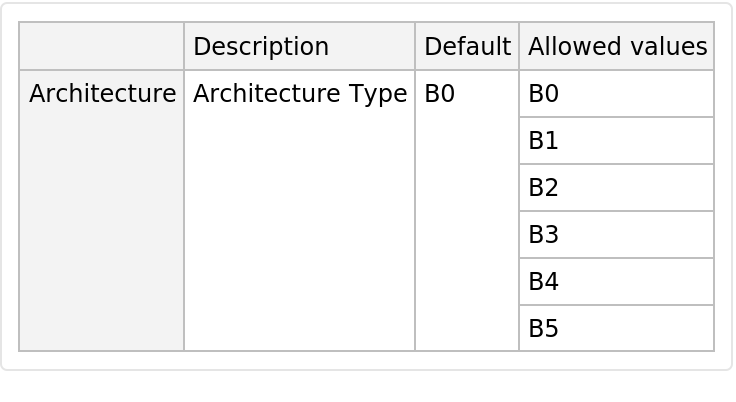
NetModel parameters
This model consists of a family of individual nets, each identified by a specific parameter combination. Inspect the available parameters:
Pick a non-default net by specifying the parameters:
Pick a non-default uninitialized net:
Basic usage
Classify an image:
The prediction is an Entity object, which can be queried:
Get a list of available properties of the predicted Entity:
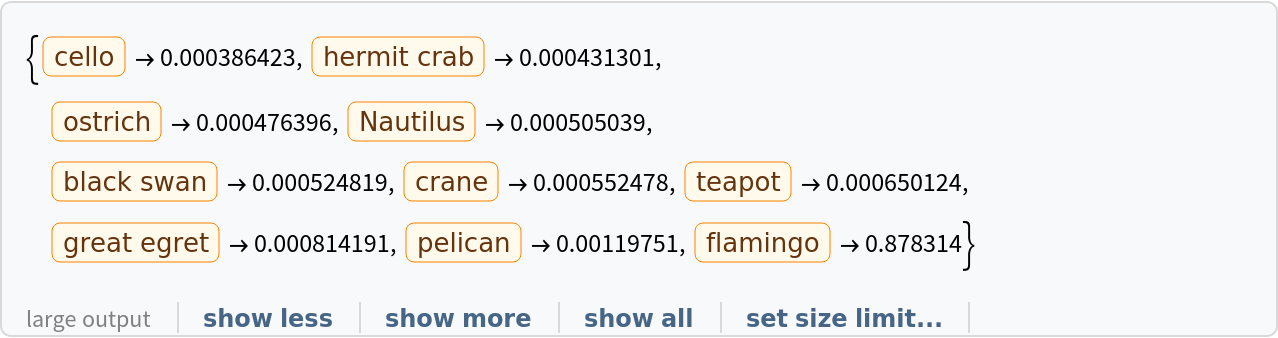
Obtain the probabilities of the 10 most likely entities predicted by the net:
An object outside the list of the ImageNet classes will be misidentified:
Obtain the list of names of all available classes:
Feature extraction
Remove the last two layers of the trained net so that the net produces a vector representation of an image:
Get a set of images:
Visualize the features of a set of images:
Visualize convolutional weights
Extract the weights of the first convolutional layer in the trained net:
Show the dimensions of the weights:
Visualize the weights as a list of 32 images of size 3x3:
Transfer learning
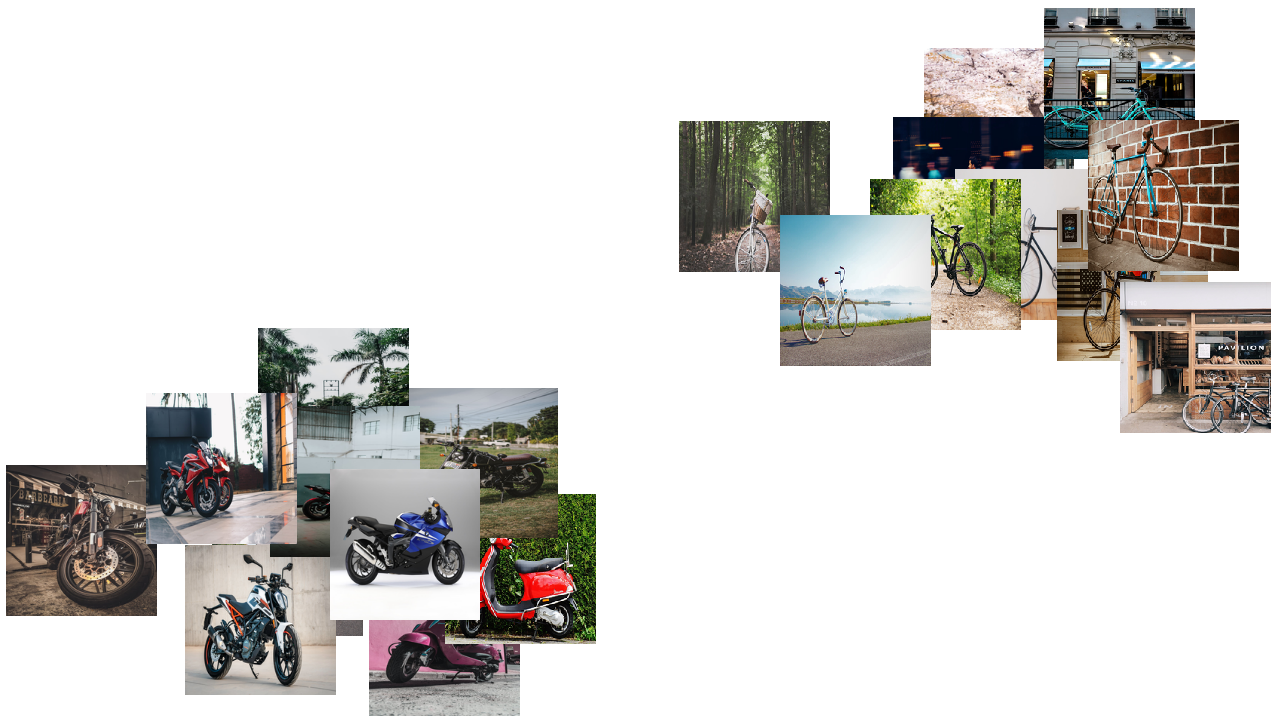
Use the pre-trained model to build a classifier for telling apart images of motorcycles and bicycles. Create a test set and a training set:
Remove the linear layer from the pre-trained net:
Create a new net composed of the pre-trained net followed by a linear layer and a softmax layer:
Train on the dataset, freezing all the weights except for those in the "linearNew" layer (use TargetDevice -> "GPU" for training on a GPU):
Perfect accuracy is obtained on the test set:
Net information
Inspect the number of parameters of all arrays in the net:
Obtain the total number of parameters:
Obtain the layer type counts:
Export to MXNet
Export the net into a format that can be opened in MXNet:
Export also creates a net.params file containing parameters:
Get the size of the parameter file:

![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/021af06e-4c1e-42e9-b694-d29dcd947319"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/4794a606ed6b3adf.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/677689c0-8469-4e34-b67e-715f8d51ee2c"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/519b20922103eaf9.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/7bd1c7df-47c8-499f-83b5-6cd72bad35df"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/2a21ffaadee0bdcd.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/eb3a80ec-5c1e-4560-b555-4f41d8d90643"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/52f9125cb90a469f.png)


![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/5e44ac16-b75c-4422-a458-336007634336"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/6525599610a1b7eb.png)
![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/27ba9f1d-5773-4240-adb8-7af28e8ec14e"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/7eacd4124354da33.png)
![newNet = NetChain[<|"pretrainedNet" -> tempNet, "linearNew" -> LinearLayer[], "softmax" -> SoftmaxLayer[]|>, "Output" -> NetDecoder[{"Class", {"bicycle", "motorcycle"}}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/39e/39e0830c-03b4-4699-84df-0f3c072f9e74/09dfe7977807480d.png)
