Resource retrieval
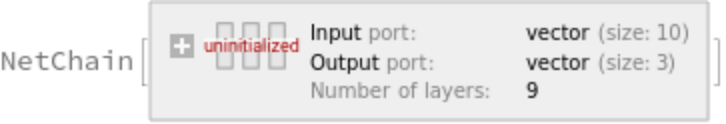
Get the uninitialized net (there are no pre-trained nets in this model):
NetModel parameters
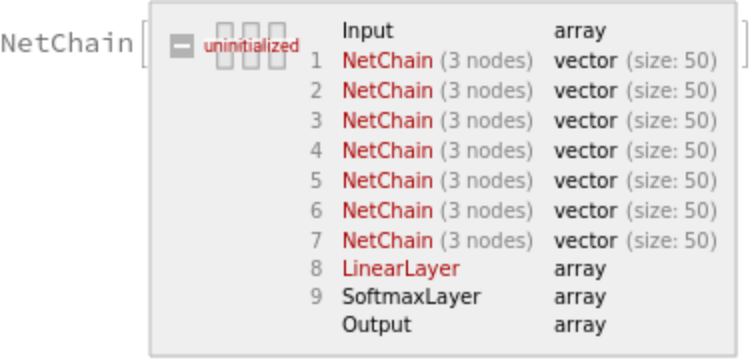
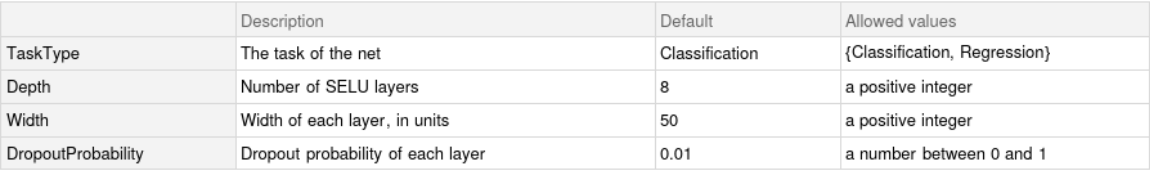
This model consists of a family of individual nets, each identified by a specific parameter combination. Inspect the available parameters:
Pick a non-default model by specifying the parameters:
Check the default parameter combination:
Basic usage
Classification on numerical data: In this example, we use an eight-layer self-normalizing network to perform classification on the UCI Letter dataset. First, obtain the training and test data:
View two random training examples:
Self-normalizing nets assume that the input data has a mean of 0 and variance of 1. Standardize the test and training data:
Get the training net:
Specify a decoder for the net:
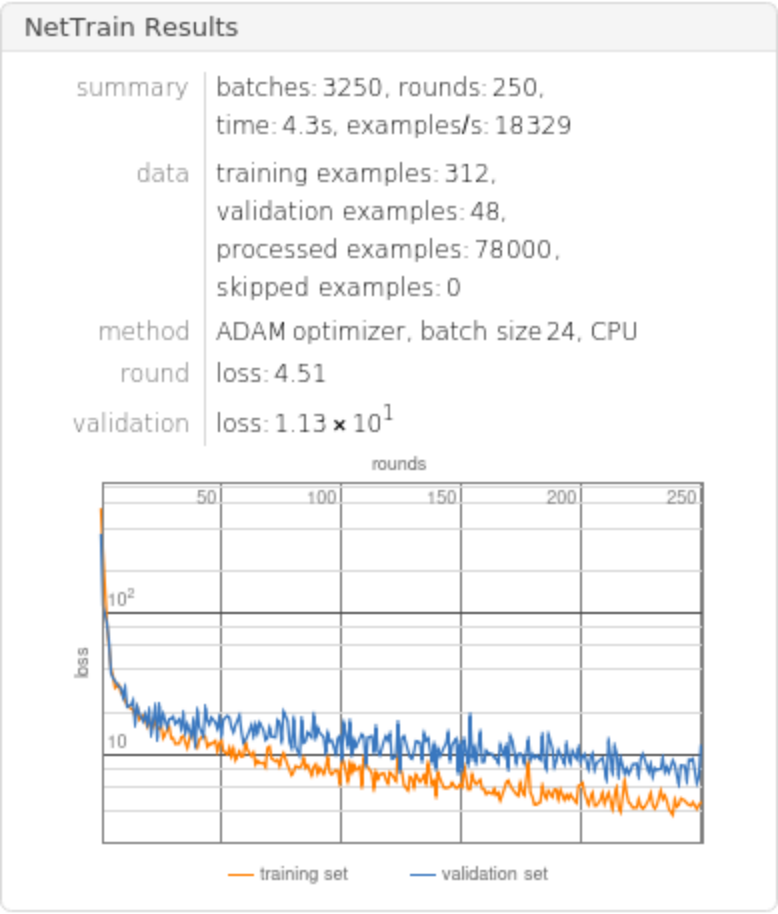
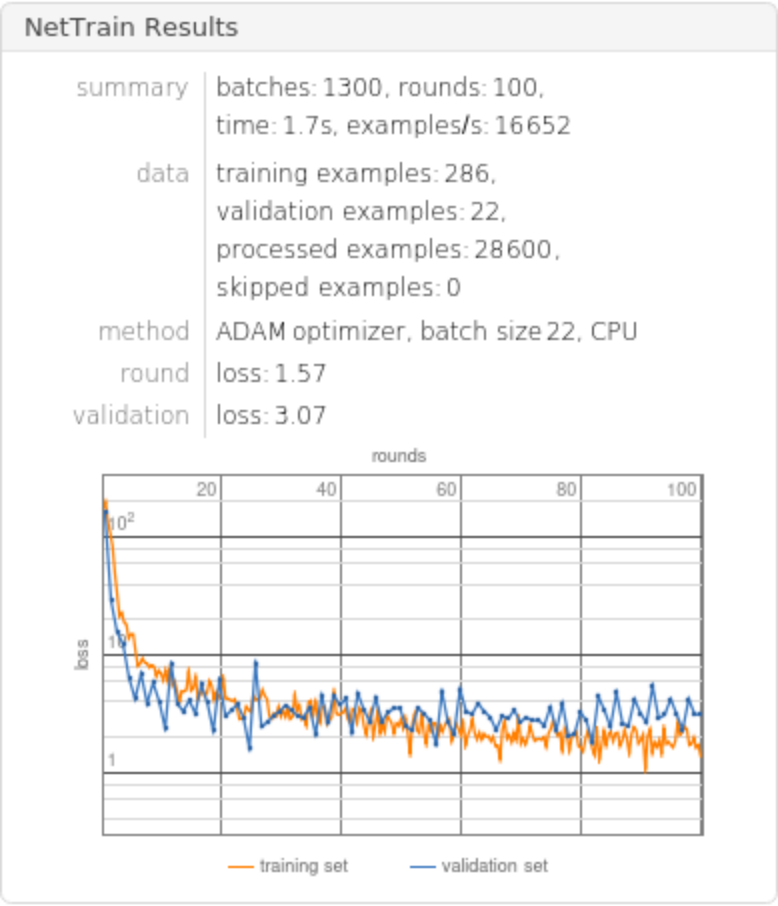
Train the net for 150 rounds, leaving 5% of the data for a validation set:
Obtain the accuracy of the trained net on the standardized test set:
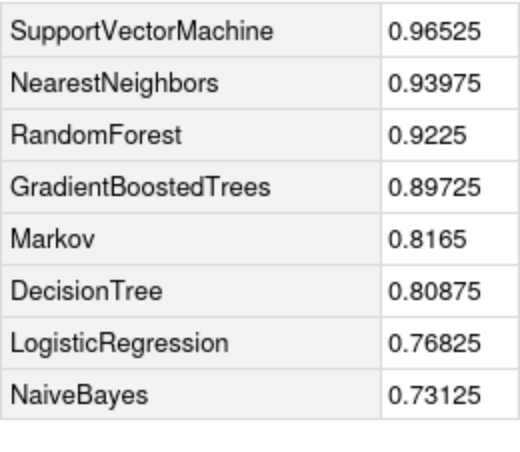
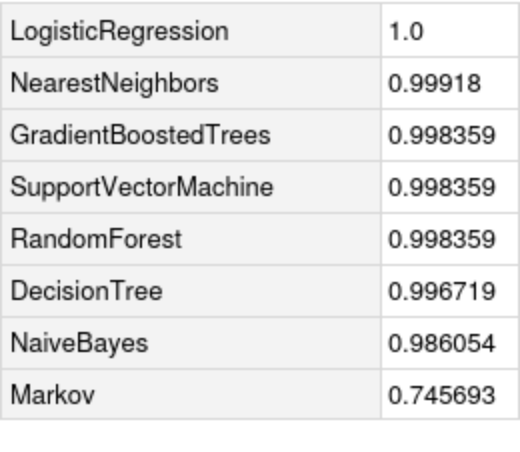
Compare the accuracy against all the methods in Classify:
Obtain a random sample of standardized test data:
Test the trained net on a sample of standardized test data:
Improving accuracy of the classifier net
Using the same example for data, first we obtain the dataset:
Standardize the test and training data in similar fashion:
Get the training net:
Specify a decoder for the net:
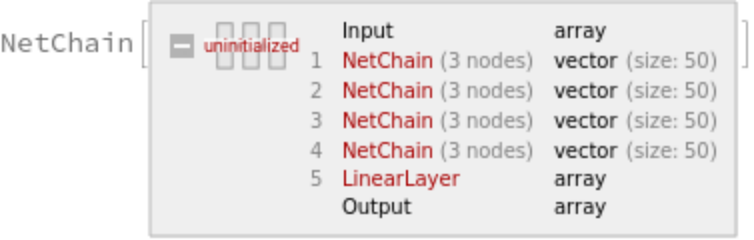
To improve the final accuracy, it is possible to average multiple trained networks obtained from different training runs. The following function runs multiple trainings and creates an ensemble network, which averages the outputs of the trained nets:
Specify the number of nets in the ensemble and create the ensemble network:
Obtain the accuracy of the ensemble network:
Compare it with the accuracy of the individual nets:
Classification on nominal data
In this example, we use an eight-layer self-normalizing network to perform classification on the Mushroom Classification dataset. First, obtain the training and test data:
View two random training examples:
To standardize this data, we first need to convert all the nominal input classes into indicator vectors:
Then standardize the numeric vectors:
Create the standardized test and training dataset:
Get the training net:
Specify a decoder for the net:
Train the net for 150 rounds, leaving 5% of the data for a validation set:
Compare the accuracy against all the methods in Classify:
Obtain a sample of standardized test data and view the actual class labels:
Test the trained net on a sample of standardized test data:
Regression on numerical data
In this example, we use an eight-layer self-normalizing network to predict the median value of properties in a neighborhood of Boston, given some features of the neighborhood. First, obtain the training and test data:
View two random training examples:
Self-normalizing nets assume that the input data has a mean of 0 and variance of 1. Standardize the test and training data:
Get the training net:
Train the net for 250 rounds leaving 7% of the data for a validation set and return both the trained net and the lowest validation loss:
Compute the test-set standard deviation:
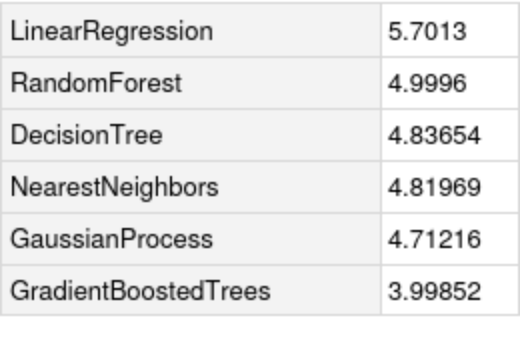
Compare the standard deviation against all the methods in Predict:
Obtain a sample of standardized test data and view the actual class labels:
Test the trained net on a sample of standardized test data:
Regression on nominal data
Create a dataset of the average monthly temperature (in degrees Celsius) as a function of the city, the year and the month:
View two random examples:
Split the data into training (80%) and test (20%) sets:
To standardize this data, we need to convert all the nominal classes to a indicator vectors:
Then standardize the numeric vector:
Create the standardized test and training dataset:
Get the training net:
Train the net for 1000 rounds leaving 7% of the data for a validation set and return both the trained net and the lowest validation loss:
Compute the test-set standard deviation:
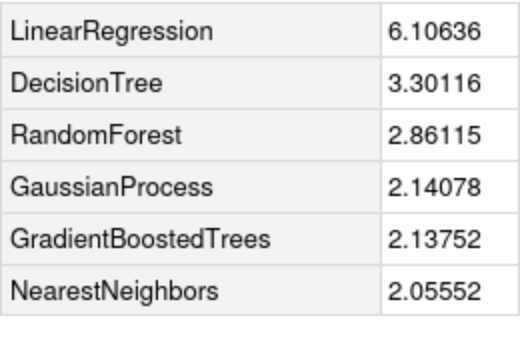
Compare the standard deviation against all the methods in Predict:
Obtain a sample of standardized test data and view the actual class labels:
Test the trained net on a sample of standardized test data:
Net information
Obtain the layer type counts:
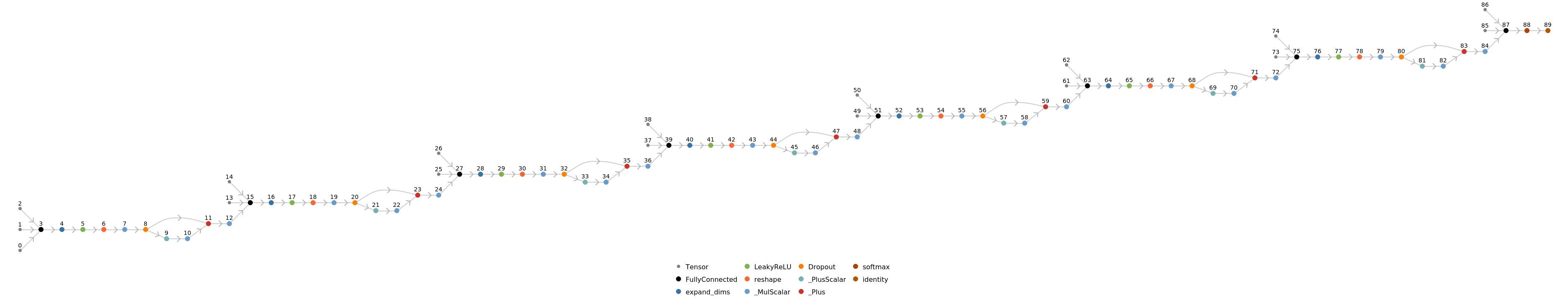
Display the summary graphic:
Export to MXNet
Export the net into a format that can be opened in MXNet. Input and output size must be specified before exporting:
Represent the MXNet net as a graph:
![extractor = FeatureExtraction[N@Keys[train], "StandardizedVector"];
trainStandardized = extractor[Keys[train]] -> Values[train];
testStandardized = extractor[Keys[test]] -> Values[test];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/3431c40c466a56af.png)
![Dataset@ReverseSort@AssociationMap[ ClassifierMeasurements[
Classify[train, Method -> #], test, "Accuracy"] &, {"RandomForest", "NaiveBayes", "SupportVectorMachine", "NearestNeighbors", "LogisticRegression", "GradientBoostedTrees", "DecisionTree", "Markov"}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/2e68eb92f3e7bea6.png)

![extractor = FeatureExtraction[N@Keys[train], "StandardizedVector"];
trainStandardized = extractor[Keys[train]] -> Values[train];
testStandardized = extractor[Keys[test]] -> Values[test];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/46f7f0a825f6ff7a.png)
![ensembleNet[n_] := Module[{ens},
ens = Table[
NetTrain[NetReplacePart[net, "Output" -> dec], trainStandardized,
ValidationSet -> Scaled[0.05],
MaxTrainingRounds -> 100,
RandomSeeding -> RandomInteger[10^6] + n ],
{i, 1, n}];
NetGraph[
{Sequence @@ ens,
TotalLayer[], ElementwiseLayer[#/N@n &]},
{NetPort["Input"] -> Range[n] -> n + 1 -> n + 2},
"Output" -> NetDecoder[{"Class", Union@Values[train]}]
]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/2f4721b87ee88368.png)
![acc = Table[
ClassifierMeasurements[
NetReplacePart[NetExtract[ensTrained, i], "Output" -> dec],
testStandardized,
"Accuracy"
],
{i, 1, n}
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/6202990e46ca4aa2.png)

![trainInputsString = Map[ToString, Keys[train], {2}];
testInputsString = Map[ToString, Keys[test], {2}]; extractor1 = FeatureExtraction[trainInputsString, "IndicatorVector"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/79f87ead43bd2fec.png)


![finalExtractor = extractor2@*extractor1; trainStandardized = finalExtractor[trainInputsString] -> Values[train];
testStandardized = finalExtractor[testInputsString] -> Values[test];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/077e400b29dbf1ee.png)
![Dataset@ReverseSort@
AssociationMap[ ClassifierMeasurements[
Classify[train,
Method -> #, PerformanceGoal -> "Quality"],
test, "Accuracy"] &, {"RandomForest", "NaiveBayes", "SupportVectorMachine", "NearestNeighbors", "LogisticRegression", "GradientBoostedTrees", "DecisionTree", "Markov"}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/763d225dfcfb9690.png)
![extractor = FeatureExtraction[N@Keys[train], "StandardizedVector"];
trainStandardized = extractor[Keys[train]] -> Values[train]; testStandardized = extractor[Keys[test]] -> Values[test];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/6ef29f19aff5534c.png)
![ReverseSort@Dataset@AssociationMap[ PredictorMeasurements[
Predict[train, Method -> #], test, "StandardDeviation"] &,
{"RandomForest", "DecisionTree", "GradientBoostedTrees", "NearestNeighbors", "LinearRegression", "GaussianProcess"}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/4923e589b79bf400.png)
![trainInputsString = Map[ToString, Keys[train], {2}];
testInputsString = Map[ToString, Keys[test], {2}];
extractor1 = FeatureExtraction[trainInputsString, "IndicatorVector"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/240432e79a4a9697.png)


![finalExtractor = extractor2@*extractor1;
trainStandardized = finalExtractor[trainInputsString] -> Values[train];
testStandardized = finalExtractor[testInputsString] -> Values[test];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/052afb9cea3d2569.png)
![ReverseSort@Dataset@AssociationMap[ PredictorMeasurements[
Predict[train, Method -> #], test, "StandardDeviation"] &,
{"RandomForest", "DecisionTree", "GradientBoostedTrees", "NearestNeighbors", "LinearRegression", "GaussianProcess"}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/0dfe155d5224053d.png)
![net = NetReplacePart[
NetModel["Self-Normalizing Net for Numeric Data"],
{"Input" -> 10, "Output" -> 3}
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/1c9/1c936c05-0e5b-49da-9d1a-163c500a907f/0f128c3416534aa8.png)