MiniLM V2 Text Feature Extractor
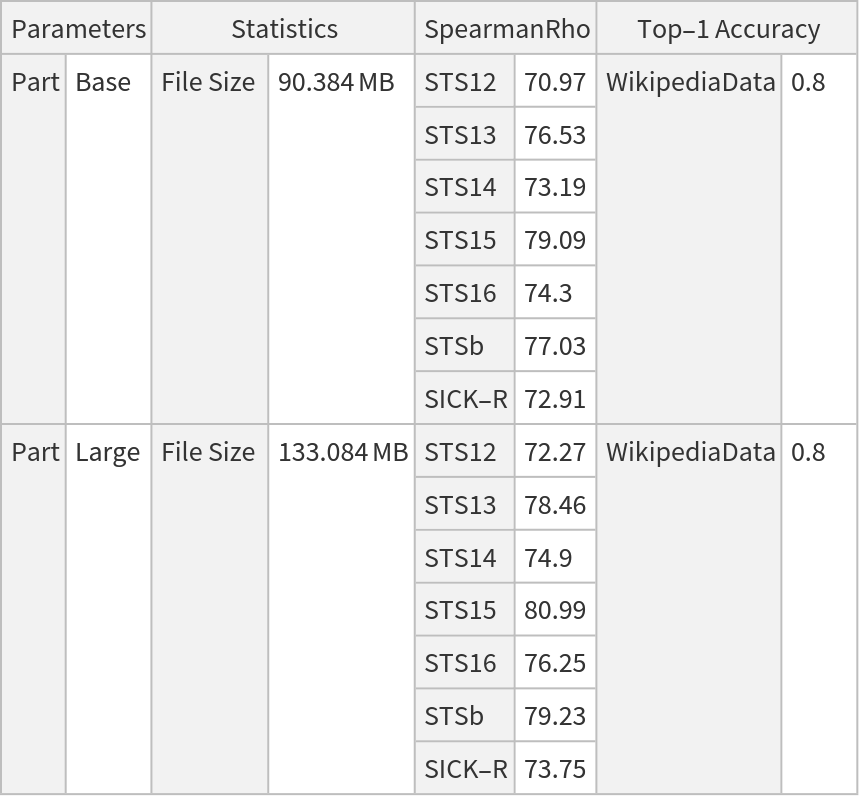
Released in 2019, MiniLM V2 is a modification of BERT designed to derive semantically meaningful sentence embeddings suitable for large-scale textual similarity tasks. It addresses a major limitation of standard BERT, which requires jointly encoding sentence pairs and is therefore computationally inefficient for semantic search or clustering. Trained on the SNLI and MultiNLI datasets, the model uses a siamese/triplet architecture with a pooling operation on top to produce fixed-size sentence embeddings that can be efficiently compared using cosine similarity.
Examples
Resource retrieval
Get the pre-trained net:
entailment
NetModel parameters
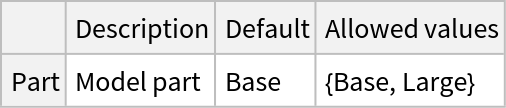
This model consists of a family of individual nets, each identified by a specific parameter combination. Inspect the available parameters:
Pick a non-default net by specifying the parameters:
Evaluation function
Get the tokenizer to process text inputs into tokens:
Write a function that preprocesses a list of input sentences:
Write a function that applies mean pooling to the hidden states:
Write a function that returns the average of the hidden states:
Basic usage
Get the sentence embedding:
Get the dimensions of the output:
Get the sentences:
Get the sentence embeddings using a non-default model:
Get the dimensions of the output:
Input preprocessing
Preprocess a batch of sentences into inputs expected by the model. The result is an association:
• "input_ids": integer token indices
• "attention_mask": a binary mask indicating valid tokens vs. padding tokens
• "token_type_ids": segment IDs used for sentence pair tasks showing which sentence each token belongs to (here all zeros since only single sentences are provided)
Get the dimensions of the preprocessed sentences:
Visualize the preprocessed sentences:
Get the sentence embeddings:
Get the dimensions of the outputs:
Visualize the first sentence embedding:
The sentence embedding is the normalized average of all non-padded token representations:
FeatureSpacePlot
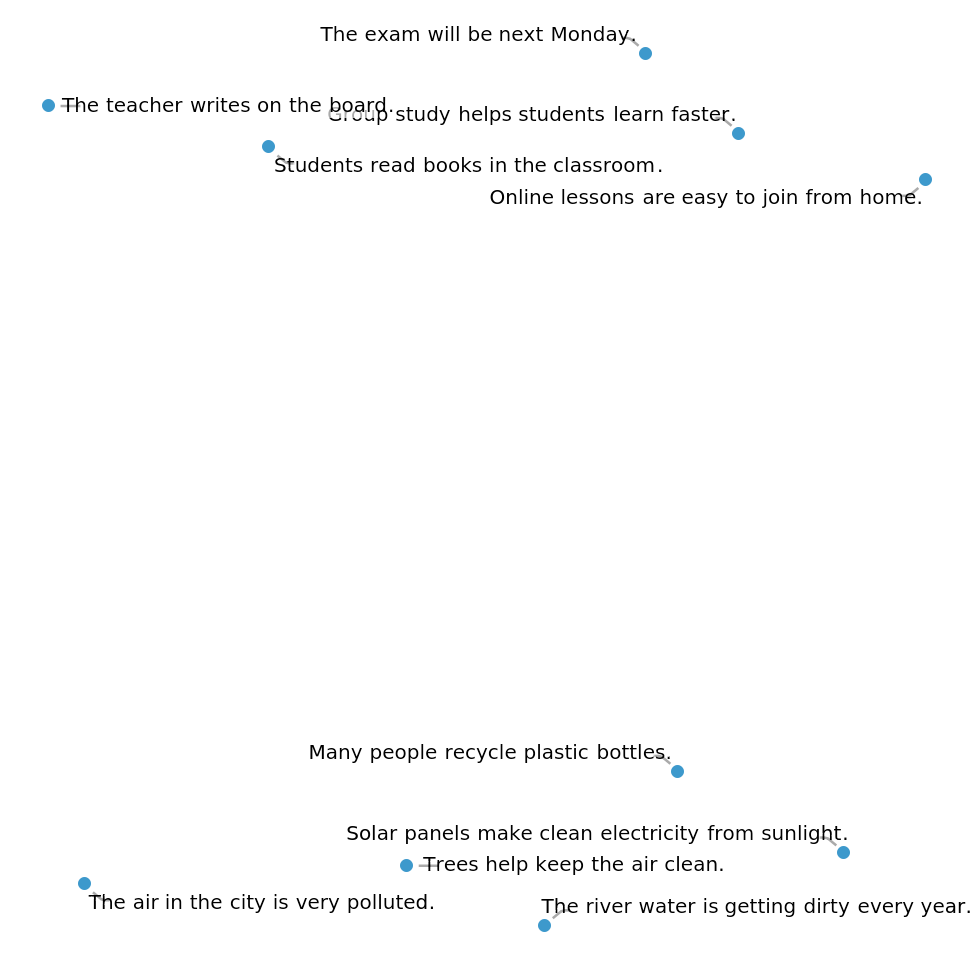
Get the sentences:
Get the embeddings of the sentences by taking the mean of the features of the tokens for each sentence:
Visualize the embeddings:
Advanced usage
One-shot learning
Get the labels with one example of each:
Get a set of sentences:
Get the embeddings of the labels and test sentences:
Get the predictions. Since all of the embeddings are normalized, SquaredEuclideanDistance, which is equivalent (up to a constant factor) to cosine distance, is used here:
Create a table to visualize the correct and predicted labels for each sentence:
Finding outliers
Get a sample of the sentences:
Get the embeddings:
Calculate the distance of each sentence embedding from the median embedding to measure how far each one is semantically:
Compute a threshold based on the median and interquartile range to detect sentences that are semantic outliers:
Find the indices for which the distance is greater than the threshold:
Get the outliers:
Document retrieval
Get the data:
Extract the text column to get the list of sentences:
Get the embeddings of the sentences:
Get a question:
Get the embedding of the question:
Find the top-three relevant tweets:
Resource History
Reference
![prepareBatch[inputStrings_?ListQ, tokenizer_ : tokenizer] := Block[
{tokens, attentionMask, tokenTypes},
tokens = tokenizer[inputStrings] - 1;
attentionMask = PadRight[ConstantArray[1, Length[#]] & /@ tokens, Automatic];
tokens = PadRight[tokens, Automatic];
tokenTypes = ConstantArray[0, Dimensions[tokens]];
<|
"input_ids" -> tokens, "attention_mask" -> attentionMask, "token_type_ids" -> tokenTypes
|>
];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/4e70ded47a812218.png)
![Options[netevaluate] = {"Part" -> "Base"};
netevaluate[inputStrings_ ?ListQ, OptionsPattern[]] := Block[
{preprocessedAssoc, embeddings, outputFeatures},
preprocessedAssoc = prepareBatch[inputStrings];
embeddings = NetModel["MiniLM V2 Text Feature Extractor", "Part" -> OptionValue["Part"]][preprocessedAssoc];
outputFeatures = meanPooler[embeddings, preprocessedAssoc["attention_mask"]];
Normalize /@ outputFeatures
];
netevaluate[inputString_ ?StringQ, OptionsPattern[]] := First@netevaluate[{inputString}, "Part" -> OptionValue["Part"]];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/587e4944c37d6832.png)





![results = Flatten@Nearest[Thread[labelEmb -> Values@labelSentences], DistanceFunction -> SquaredEuclideanDistance][inputEmb];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/2d2253304eebe185.png)
![Grid[Prepend[
Transpose[{Keys@testSentences, Values@testSentences, results}], {"Text", "True Label", "Predicted Label"}], Frame -> All, Background -> {None, {LightGray}}, Alignment -> Left]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/7f772efd1d1d66af.png)

![movieData = {"The movie received great reviews from critics and audiences.", "The actor delivered an outstanding performance in the film.", "The director created a powerful story with deep emotions.", "The soundtrack perfectly matched the tone of the movie.", "Critics praised the movie for its realistic characters.", "The new film attracted millions of viewers worldwide.", "The main character faced many challenges in the plot.", "The audience applauded at the end of the movie.", "The film\[CloseCurlyQuote]s trailer got millions of views in one day.", "The team celebrated their victory in the final match.", "A new smartphone model was released with advanced features.", "The weather forecast predicts heavy rain for the weekend.", "Students are preparing for their final exams this month." };](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/0a7bc672ddf50049.png)
![distance = DistanceMatrix[movieEmb, {Median[movieEmb]}, DistanceFunction -> SquaredEuclideanDistance][[All, 1]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/4b1c960f8e67fe4f.png)

![Nearest[Thread[vecData -> dataText], questionEmb, 3, DistanceFunction -> SquaredEuclideanDistance] // Column](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/146/1465be9e-f515-48f5-a9cb-49f48d914468/1d2843697d91a96a.png)
